

POLYGON/THREAD MILLING
|
"Polygon" Attachments are used on a cross slide to produce flats, polygons, threads and certain slots in round material without stopping the spindle. |
|
|
These operations are best suited for non-ferrous materials because of the very high surface cutting speed developed by the cutter. |
|
Usually the flats are done with a plunging operation using a form tool cam. On machines or attachments with axial movement, the flats can be machined by longitudinal turning, which facilitates extra wide flats or flats in difficult materials. |
|
|
Some companies do flat generation in mild steels, but they are willing to accept very low insert life. Thread milling will not work in steel. |
|
|
Polygon cutters use carbide inserts, either single edge re-sharpenable or multi-edge throw-away types. |
|
|
Thread Milling cutters are HSS and have the thread form ground on the O.D. This way you can make virtually any thread in non-ferrous materials, even tapered or close to a shoulder. No shaving is required before thread milling. |
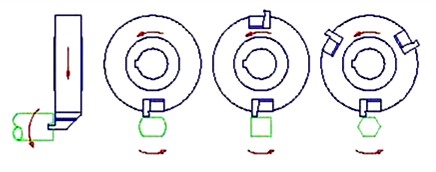
2:1 Cutter RPM makes the flattest flats for an even number of flats
THREAD MILLING/ODD
FLATS OR SLOTS

1:1 Cutter RPM for thread milling and odd numbers of flats (will be some convexity)

Reverse 1:1 Cutter RPM to make slots in ball valves
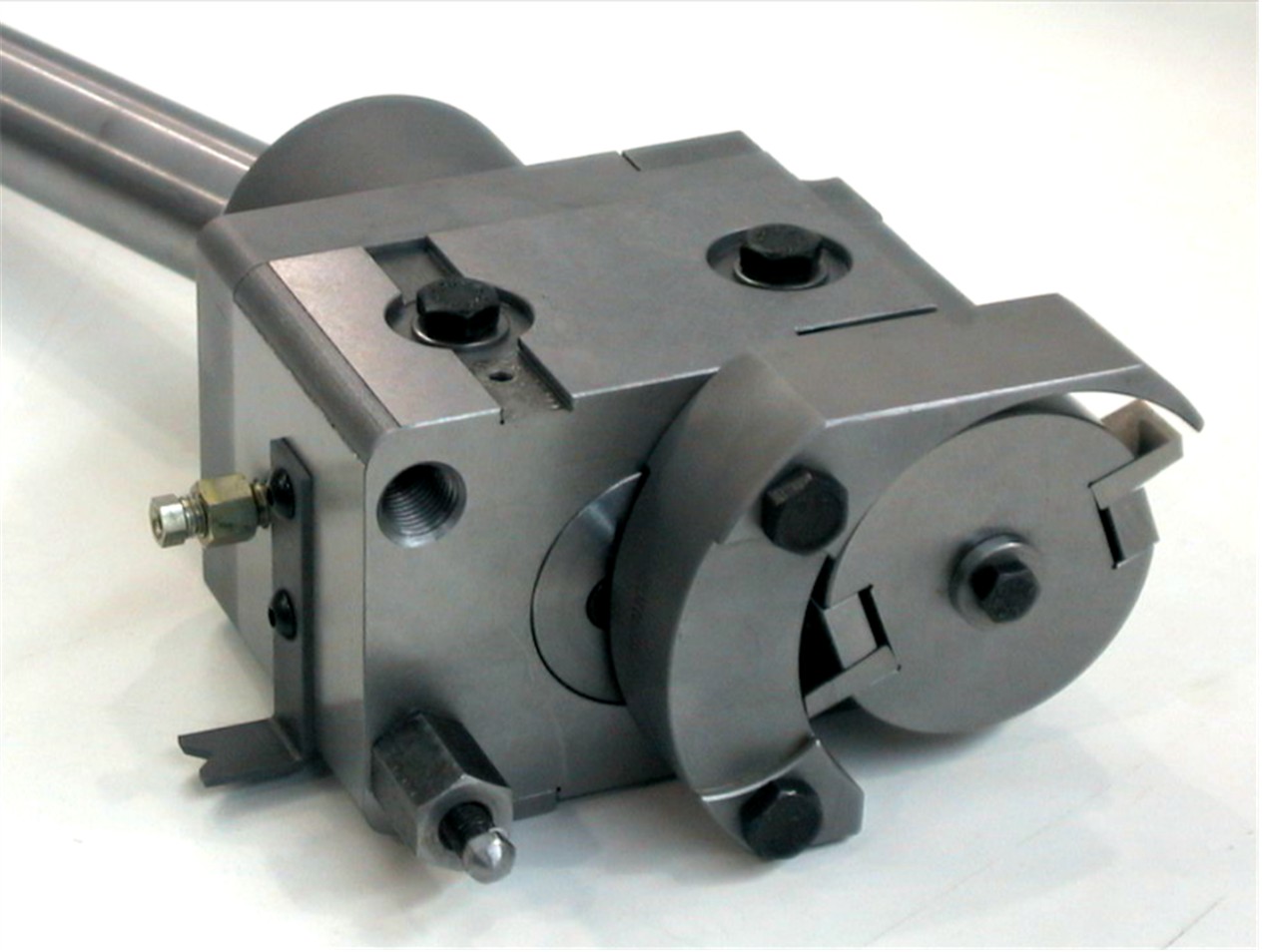

Typical Cutter Gear Box and Head, also shown in a machine